Logical Data Warehouse: All you Need to Know

Discover key concepts and the architecture behind a logical data warehouse. Learn the difference with traditional data warehouses.
In this post, we’ll explain what a logical data warehouse is and how it can help simplify the management process when dealing with large amounts of structured and unstructured data. We’ll also discuss key points such as scalability, flexibility, cost savings, integration benefits, and more. So if you’re ready to learn all that’s necessary when considering a logical data warehouse solution – don’t miss this infographic with insights from S2E!
What is a Logical Data Warehouse?
Logical Data Warehouses (LDW) allow organizations to break free from traditional data warehousing approaches and access an array of sources, such as relational databases, Hadoop-LIKE clusters, or NoSQL databases in real-time.
This virtual layer abstracts physical storage to enable direct integration without the need for ETL. Through SQL interfaces, REST APIs, or web portals users have flexible options to analyze their data using visual tools like Tableau QlikView, etc. Furthermore, they may also include cloud services such as Salesforce Google Analytics & Twitter into this infrastructure.
Check out the infographic below to discover how S2E developed a Logical Data Warehouse and how they applied it successfully in a project for Hippocrates Holding!
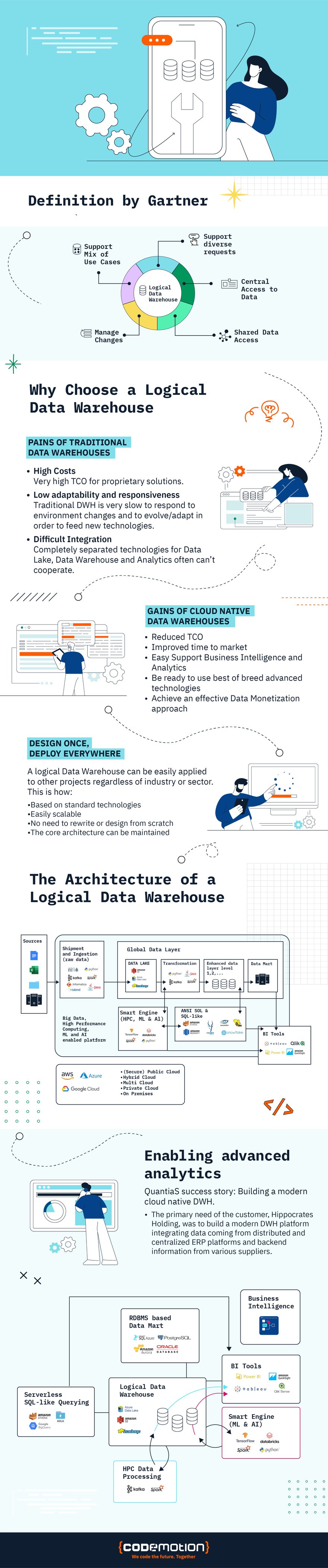
Logical Data Warehouse vs Traditional Data Warehouse
In the world of data warehousing, a traditional approach involves a lengthy process of data extraction, transformation, and loading into a central repository. While this approach still holds value, it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Enter, the LDW – a flexible, virtual alternative to traditional data warehousing.
Here are the key differences:
Data Integration – data is integrated virtually, granting access directly from its source, sans ETL processes
Data Structure – data is flexible in its organization, allowing for more dynamic querying and analysis than traditional schemas
Data Storage – data can be stored across a variety of sources including databases, Hadoop-LIKE clusters, and cloud-based services
Data Processing – batch processing gives way to real-time or near-real-time processing, supporting timely and accurate data analysis
Data Access – exceeds traditional data warehousing, providing a user-friendly variety of interfaces and tools for querying and analysis.
But be aware, while the LDW offers greater agility and a faster response time, implementing one requires advanced technical skills and is more complex than traditional approaches.
QuantiaS success story: Building a modern cloud-native DWH
As an S2E company, QuantiaS is a business and technology consultancy group that specializes in professional services related to digital transformation, cloud adoption, cybersecurity, and data and analytics. With more than 350 professionals, the company has had one of the highest growth rates among Italian firms over the last two years.
QuantiaS uses its technological expertise to help IT managers and company executives make sense of the vast amount of data generated by their organization. By adopting a top-down approach to data management, stakeholders can uncover valuable insights and opportunities to stay ahead of the competition.
For a project with Hippocrates Holding, a network of pharmacies and health-related companies based in Milan, Quantias built a modern DWH platform based on the information shared in the infographic above, enabling the client to integrate data coming from distributed and centralized ERP platforms and various suppliers information back end.
.
Fonte: Codemotion





Riempi il Form sottostante per poter lasciare i tuoi commenti